Petrophysics Suite
Laminated Sand Analysis (LSA)
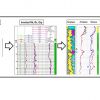
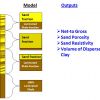
The Laminated Sand Analysis model consists of alternating sand and shale laminations. LSA computes net-to-gross for the interval and key properties of the sands. LSA utilizes an industry standard bimodal model of alternating sand and shale laminations, with dispersed clay in the sand laminations.
Plug-in Overview
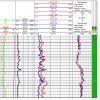
The Petrophysics Suite includes Rt Scanner processing, Rt Scanner based fracture detection (TL 2016+) and Laminated Sand Analysis (LSA). Rt Scanner Inversion computes vertical resistivity (Rv), horizontal resistivity (Rh) and formation dip. Rv and Rh are free of bed boundary effects, dipping bed effects, and can be used for thin bed analysis in LSA. The dips are useful for reservoir mapping.
Specifications
Runs on Techlog 2015.3 or higher
Rt Scanner Inversion outputs
- Vertical and horizontal resistivity, formation dip and azimuth from the 1D inversion
Laminated Sand Analysis outputs
- Sand and laminated shale fractions
- Sand fraction resistivity and porosity
- Water volume and saturation in laminated sand
New for TL 2016: Vertical Fracture Detection Outputs
- Vertical fracture detection and fracture orientation Applications
- Evaluate sandstone or carbonate reservoirs with conductive lamination's
- Define intervals for perforation Detect zones of lost circulation
- Select intervals for further evaluation via MDT, MSCT, MR Scanner, Dielectric Scanner
- Formation Dip
Features
In thin beds, water saturations from conventional analysis are too high. Using Rh & Rv in Laminated Sand Analysis, an accurate analysis is achieved. LSA accepts Rv & Rh from any service company or tool type. Overbalanced drilling can lead to lost circulation into induced vertical fractures. Rt Scanner fracture detection identifies where the mud was lost and fracture orientation.